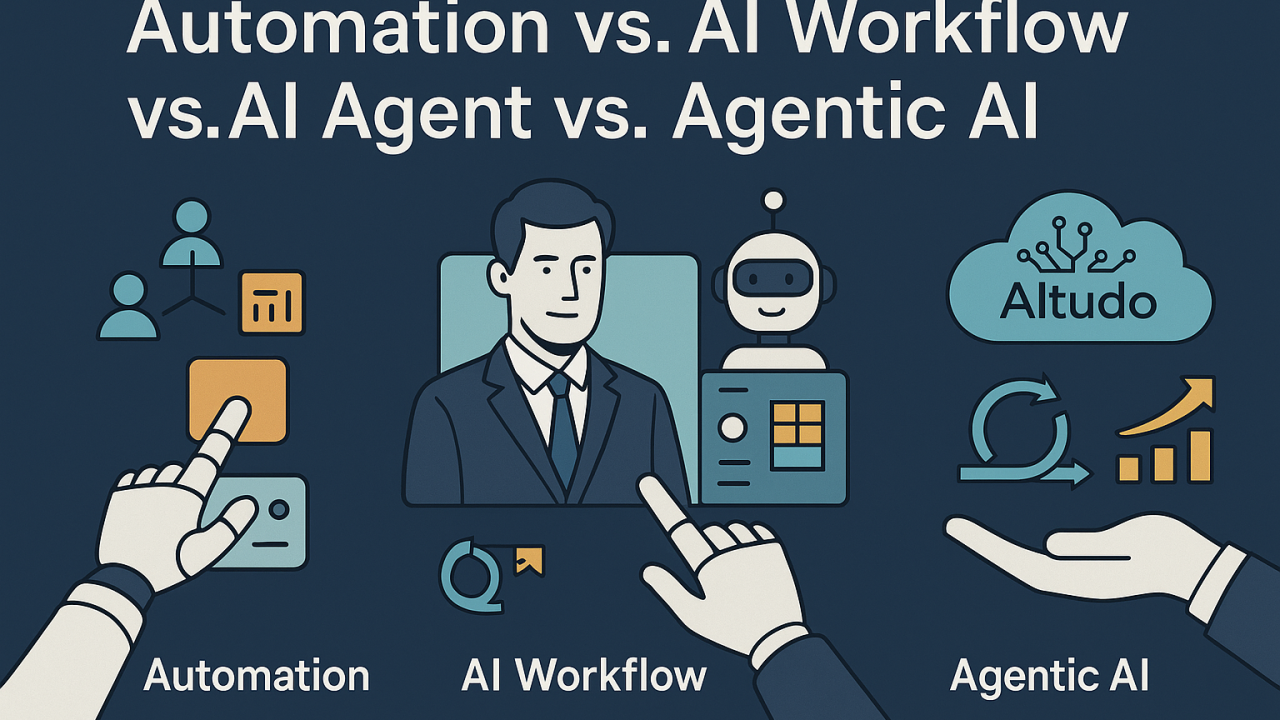
In today’s whirlwind of tech buzzwords, it’s easy to feel like automation, AI workflows, AI agents, and Agentic AI are all just fancy ways of saying “robots doing stuff.” Spoiler: they’re not. Each plays a completely different game — from simple task-doers to decision-making, goal-chasing digital minds.
If you’re aiming to stay relevant and not become obsolete in this AI madness, understand the isn’t just nice to have, it’s mission-critical. In this blog, I’ll break down what each really means, where they shine, where they stumble, and throw in real-world examples and best practices to keep it all grounded (and jargon-free).
Understanding the Basics
1. Automation
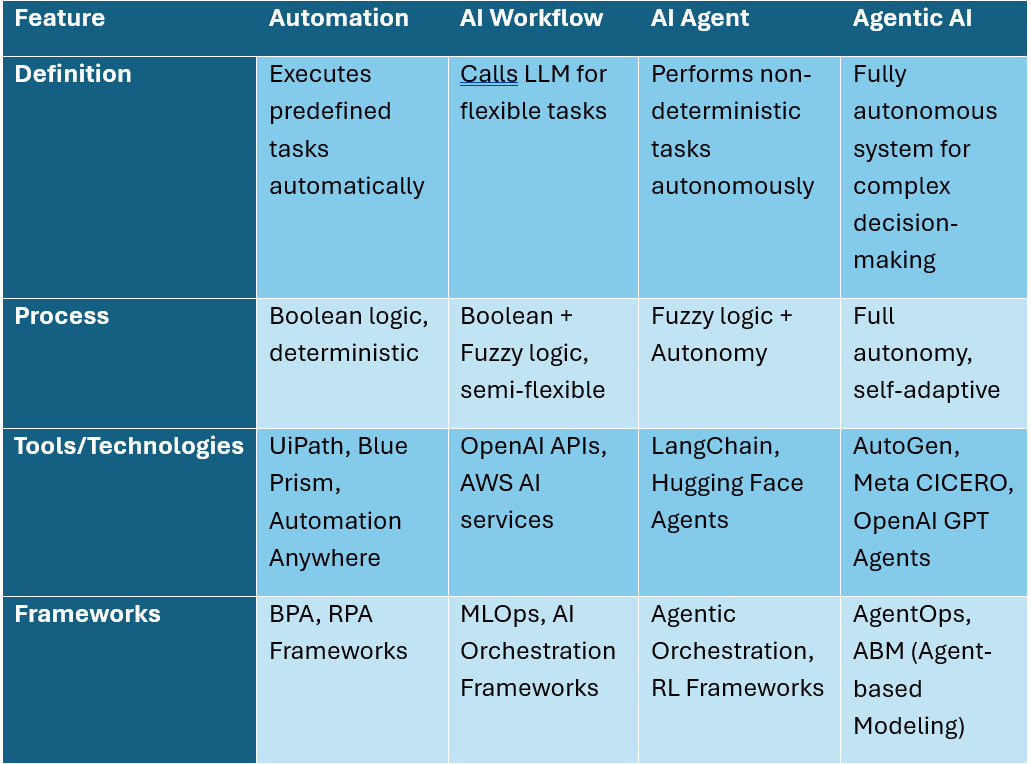
Definition: Automation involves programs that execute predefined, rule-based tasks automatically without any variation.
- Process: Follows strictly Boolean logic with deterministic paths.
- Tools/Technologies: RPA (Robotic Process Automation) tools like UiPath, Blue Prism, Automation Anywhere.
- Frameworks: Business Process Automation (BPA) frameworks.
2. AI Workflow
Definition: An AI workflow calls a large language model (LLM) via an API for one or more flexible steps, improving pattern recognition.
- Process: Combines Boolean logic with Fuzzy logic.
- Tools/Technologies: OpenAI API, Hugging Face transformers, AWS AI services.
- Frameworks: MLOps pipelines, AI orchestration frameworks.
3. AI Agent
Definition: An AI agent is designed to perform non-deterministic, adaptive tasks autonomously, simulating human-like behavior.
- Process: Driven by Fuzzy logic + Autonomy.
- Tools/Technologies: LangChain, AutoGPT, Hugging Face Agents.
- Frameworks: Agentic orchestration platforms, Reinforcement Learning frameworks.
4. Agentic AI
Definition: Agentic AI represents a broader, more advanced system capable of independent decision-making, multi-agent collaboration, and continuous learning.
- Process: Full autonomy, goal-driven, adaptive multi-agent systems.
- Tools/Technologies: OpenAI’s GPT Agents, Meta’s CICERO AI, Microsoft’s AutoGen.
- Frameworks: Agent-based modeling (ABM), AgentOps platforms.
Comparison Table: Automation vs AI Workflow vs AI Agent vs Agentic AI
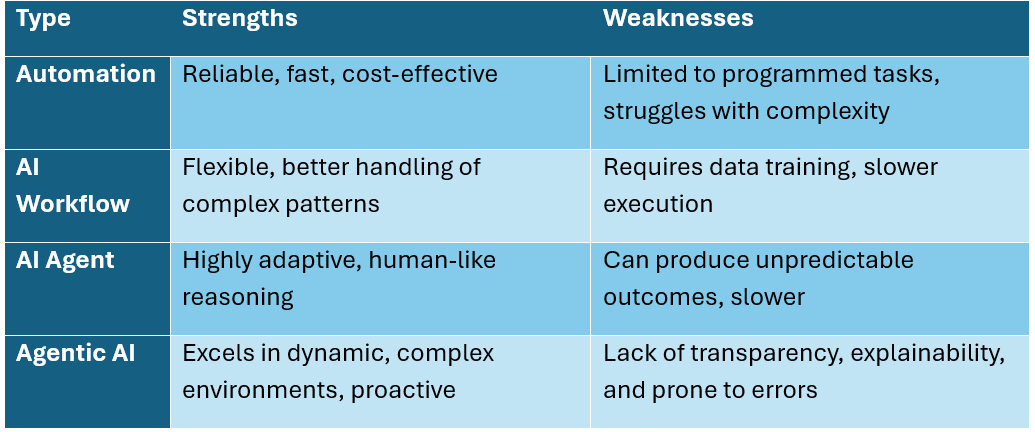
Strengths and Weaknesses Across Systems
Industry Insights: Where Are We Heading?
According to a recent report by McKinsey, Agentic AI will power the next phase of automation — “decision-making at machine speed.” Industries like healthcare, automotive, and customer service are already seeing early adoption through autonomous vehicles, virtual agents, and dynamic task orchestration.
Some noteworthy applications:
- Healthcare: AI agents recommending personalized treatment plans.
- Manufacturing: Autonomous drones handling warehouse logistics.
- Customer Support: Agentic AI handling customer queries with self-adaptive reasoning.
The future points toward increasingly decentralized, goal-driven AI ecosystems where multiple agents collaborate autonomously without constant human supervision.
As businesses evolve, understanding the distinct capabilities of Automation, AI Workflows, AI Agents, and Agentic AI will determine who leads and who lags behind. The shift from simple automation to complex agentic systems marks not just a technological upgrade — it’s a fundamental transformation in how enterprises operate.
Choosing the right technology depends on the nature of tasks, desired flexibility, risk appetite, and the strategic importance of autonomy